Enterprise resource planning
The management concept proposed by Gartner Group Inc, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), is based on information technology and provides a management platform for decision-makers and employees to make decisions through a systematic management approach. Proposed by Gartner Group in 1990. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is the next-generation manufacturing system and resource planning software of MRP II (Enterprise Manufacturing Resource Planning). In addition to the existing production resource planning, manufacturing, finance, sales, procurement and other functions of MRP II, there are also quality management, laboratory management, business process management, product data management, inventory, distribution and transportation management, human resource management, and periodic reporting system. The meaning represented by ERP in our country has been expanded, and all types of software used in enterprises have been included in the scope of ERP. It breaks away from the boundaries of traditional enterprises and optimizes enterprise resources from the scope of the supply chain, based on the new generation of information systems in the era of network economy. It is mainly used to improve business processes in enterprises to enhance their core competitiveness. ERP is a supply chain management concept proposed by Gartner Group Inc, a computer technology consulting and evaluation group in the United States. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) refers to a management platform established on the basis of information technology, which provides decision-making and operational means for enterprise decision-makers and employees with a systematic management philosophy. The ERP system supports mixed manufacturing environments such as discrete and process oriented, and its application scope has expanded from manufacturing to retail, service, banking, telecommunications, government agencies, and schools. By integrating database technology, graphical user interfaces, fourth generation query languages, client server structures, computer-aided development tools, and portable open systems, it effectively integrates enterprise resources.
-

The primary function of financial management is based on accounting data, further analyzed to carry out corresponding forecasting, management, and control activities. It focuses on financial planning, control, analysis, and forecasting:
-
Financial Planning: Developing financial plans and budgets for the upcoming period based on previous financial analysis.
-
Financial Analysis: Providing query functionality and assessing financial performance through graphical displays of user-defined variance data, including account analysis.
-
Financial Decision-Making: The core component of financial management, involving decisions related to funds, including fundraising, investment, and fund management.
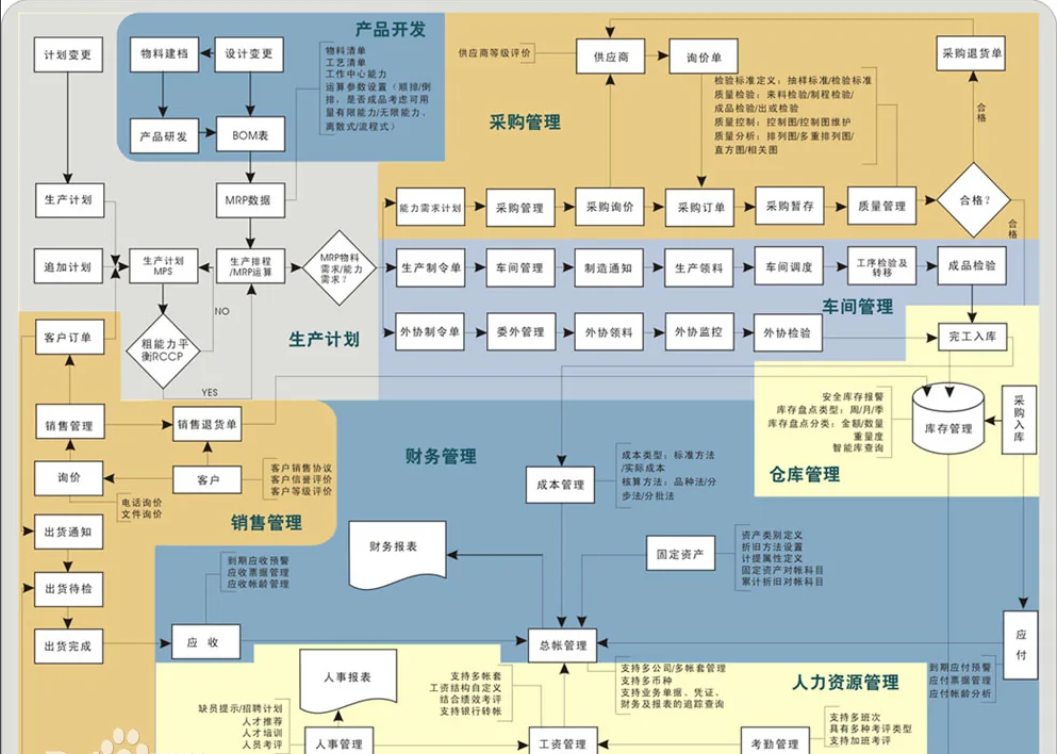
The Production Control Management module is the core of the ERP system. It organically integrates the entire production process of the enterprise, enabling effective reduction of inventory and improved efficiency. The automatic connection of previously scattered production processes ensures a coherent production flow, avoiding production gaps and delays in delivery times.
If you would like me to continue with the translation, please let me know.
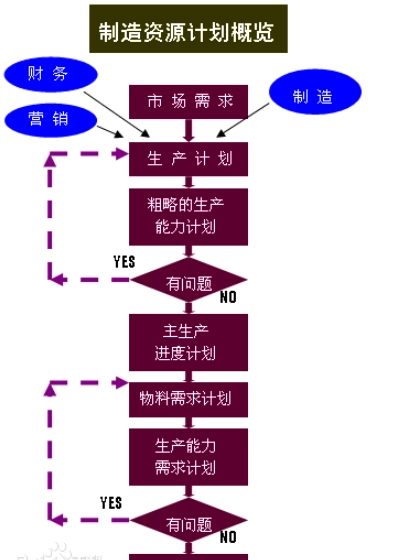
This is an advanced production and management method guided by planning. First, the company establishes a total production plan, which is then further subdivided through systematic processes and delegated to various departments for execution. Each department, such as production and procurement, follows this plan. The main content overview of production control management is as follows:
-
Master Production Planning (MPS): Based on production plans, forecasts, and customer orders, it arranges the types and quantities of products provided in each future cycle. It transforms production plans into detailed schedules, precise in terms of time and quantity, balancing material and capacity needs.
-
Material Requirements Planning (MRP): After determining how much final product to produce based on the master production plan, it converts the quantity of products to be produced into the required quantities of components. By comparing with existing inventory levels, it determines the additional processing and procurement quantities needed.
-
Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP): After generating a preliminary material requirements plan, it creates detailed work plans by balancing the total workload of all work centers with their capacities. This ensures that the generated material requirements plan is feasible in terms of the enterprise's production capacity.
-
Shop Floor Control: It involves dynamic job scheduling that changes over time, allocating tasks to specific workshops, followed by job sequencing, management, and monitoring.
-
Manufacturing Standards: In planning, various production basic information, known as manufacturing standards, is needed. These include part codes, product structures, processes, and work centers, identified by unique codes in the computer system.
ERP, with its emphasis on planning, integrates customer demands and internal manufacturing activities, forming a complete supply chain. Its core management philosophy is reflected in three main aspects: managing the entire supply chain resources, incorporating lean production, agile manufacturing, and synchronous engineering concepts, and emphasizing pre-planning and pre-control.
The success of ERP application is marked by integrated system operations, streamlined business processes, dynamic performance monitoring, and continuous improvement in management. ERP offers significant features such as integration, systematization, flexibility, and real-time control.
ERP in China faces challenges such as the use of unfamiliar terminology and the lack of standardized implementation methods. Successful ERP implementation relies on effective decision-makers, thorough consultation and research, and careful selection of suitable ERP software considering various factors. ERP systems based on the supply chain management philosophy demand attention to key aspects during implementation to ensure success.
Please let me know if you want me to continue with the translation or if there's anything specific you'd like to focus on.
-