What does ERP mean
ERP is the abbreviation for Enterprise Resource Planning, which is an integrated management software system aimed at helping enterprises achieve effective management and optimization of resources. This article will provide a detailed explanation of ERP from multiple aspects, including definition, functionality, implementation process, etc.

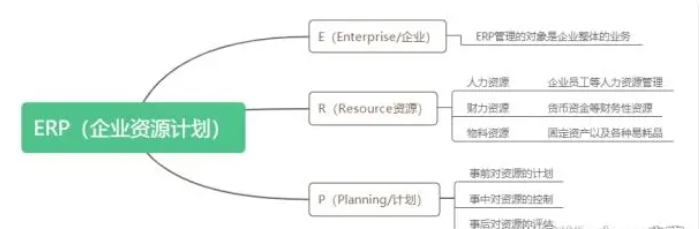
Tool materials: Computer brand and model: Dell XPS 15 Operating system version: Windows 10 Software version: SAP ERP 6.0 1. Definition of ERP 1. What does ERP mean? ERP, abbreviated as Enterprise Resource Planning, is an integrated management software system. It is a comprehensive management tool and information system software. The ERP system aims to help organizations integrate, optimize, and manage various internal resources of the enterprise, including human resources, financial funds, material inventory, production planning, etc. This system provides an integrated platform to assist enterprises in cross departmental data sharing and process coordination, improve business efficiency, optimize resource utilization, improve product quality, optimize supply chain and customer relationships, etc. ERP systems typically include many modules and functions, such as financial accounting, supply chain management, production management, sales and marketing, human resource management, etc. By integrating various functions and processes, ERP systems can provide comprehensive management and decision support for enterprises, promoting their scale, standardization, and sustainable development. Integrate the financial, procurement, production, sales, inventory and other business functions of the enterprise into an information management platform. Each department can connect with other departments through the EPR system, and business processing can be done in real-time online. For example, business personnel can directly access the required internal data through the system and connect with customers, without the need to go to other departments to collect data. Business data can be queried online. Implementing enterprise resource control, also known as EPR.
2. The origin and development of ERP was proposed by Gartner Group Inc in the early 1990s. It evolved from the MRP (Material Requirements Planning) system that began to be used in the 1960s. Integrating material management, financial management, value management, and human resources into enterprise performance, maximizing the utilization of enterprise resources to improve efficiency.
According to the development history of ERP, its functionality has gradually improved over time, extending beyond traditional management of human, material, and resource aspects. Through integrated systems, optimized processes, and collaborative workflows, ERP transforms the operation of enterprises into an organic whole. It permeates information technology into various aspects of enterprise production and operations.
3. Basic Characteristics of ERP:
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is an integrated management software system designed to coordinate operations and processes across different departments and functions within an enterprise. The basic characteristics of ERP include:
-
Integration:
- ERP integrates various enterprise functional modules such as finance, logistics, sales, procurement, and production.
- This integration facilitates data sharing and circulation between different modules, enhancing internal collaboration efficiency.
-
Uniformity:
- ERP provides a unified data storage and management platform, allowing departments and functions to view and analyze data within the same system.
- This eliminates data redundancy and inconsistency, promoting information sharing and communication.
-
Real-Time:
- ERP systems offer real-time data updates and reports, aiding timely decision-making for management.
- Departments can use real-time data in the system to understand the operational status of the enterprise, facilitating better planning and management.
-
Scalability:
- ERP systems can be customized and expanded according to the needs of the enterprise.
- Businesses can add or modify modules based on their specific business requirements, adapting to changes and expansions.
-
Standardization:
- ERP systems are designed based on industry standards and best practices, following norms and standards.
- This helps enterprises improve the efficiency and quality of business processes, allowing comparison and communication with other businesses.
-
Automation:
- ERP systems automate and optimize business processes, reducing manual operations and errors.
- Automation enhances production efficiency, lowers costs, and provides faster service and response times.
In summary, the basic characteristics of ERP include integration, uniformity, real-time capability, scalability, standardization, and automation. These features make ERP a powerful tool for managing enterprise resources and processes, helping businesses improve efficiency and competitiveness.
2. ERP Functions:
-
Comprehensive Management:
- ERP systems integrate and manage various resources, including human resources, financial resources, logistics resources, and production resources.
- Centralized management improves resource utilization efficiency and collaborative operational capabilities.
-
Business Process Management:
- ERP systems manage and optimize various business processes, including sales, procurement, inventory management, and production planning.
- Automation and standardized processes enhance work efficiency and accuracy.
-
Data Integration and Sharing:
- ERP systems integrate and share data from different departments and systems, ensuring real-time information updates and circulation.
- This reduces redundant work and data redundancy, aiding more accurate analysis and decision-making.
-
Financial Management:
- ERP systems manage the financial processes and accounting of the enterprise, including accounting processing, report generation, cost control, and budget management.
- Centralized management and analysis of financial data provide accurate financial information and decision support.
-
Supply Chain Management:
- ERP systems manage the enterprise's supply chain, including supplier management, logistics management, and inventory control.
- Comprehensive monitoring and planning of the supply chain improve delivery capabilities and reduce costs.
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- ERP systems assist in managing and interacting with customers, including sales opportunity tracking, customer service management, and marketing.
- Building and maintaining a customer information database improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In conclusion, ERP systems help enterprises integrate resources, manage processes, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance service quality, thereby strengthening competitiveness and achieving long-term sustainable development.
3. ERP Implementation Process:
-
Needs Analysis:
- Clarify the enterprise's needs and goals, understand current business processes and system conditions.
- Determine the required functions and customization needs for the ERP system through communication and research with various departments.
-
Selecting a Vendor:
- Based on the results of needs analysis, screen and choose an ERP vendor suitable for the enterprise.
- Consider factors such as the vendor's implementation experience, technical capabilities, industry adaptability, and service support.
-
Project Planning:
- Determine the project schedule, budget, and resource allocation, and create a detailed project plan.
- This includes plans for personnel training, data migration, and testing.
-
System Customization and Configuration:
- Customize and configure the ERP system according to the results of needs analysis.
- Modify system settings, write custom code, and create reports to meet specific business needs.
-
Data Migration:
- Migrate existing data from the old system to the new ERP system.
- This involves cleaning, converting, and validating data to ensure its integrity and accuracy.
-
System Integration:
- Integrate the ERP system with other enterprise systems (such as financial and human resources systems) to ensure seamless data and process connections.
- Interface development and system integration may be required.
-
Testing and Training:
- Conduct various tests, including functional testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing.
- Train system administrators and end-users to proficiently use the new system.
-
Go-Live and Support:
- Conduct final system backups and security tests before going live.
- After implementation, provide ongoing technical support and maintenance, addressing issues and optimizing the system.
The ERP implementation process requires professional guidance and management, as well as effective communication and coordination. While each enterprise's implementation process may vary, the outlined steps represent a general implementation flow. For larger projects, the process may be more complex and time-consuming.
4. Value of ERP:
-
Process Integration and Collaboration:
- ERP systems integrate various business processes across different departments, optimizing information sharing and collaboration.
- By providing unified data and standardized processes, ERP eliminates information silos and repetitive tasks, improving work efficiency.
-
Data Integration and Accuracy:
- ERP systems integrate data from various departments, forming a unified data source.
- This avoids duplicate data entry and inconsistency, enhancing data accuracy and reliability, providing reliable data support for decision-making.
-
Real-Time Monitoring and Analysis:
- ERP systems can monitor enterprise operations in real-time, including sales, procurement, production, inventory, and more.
- Through ERP's reporting and analysis functions, enterprise management can promptly understand the operational status, making effective decisions.
-
Cost Control and Efficiency Improvement:
- ERP systems optimize enterprise processes and resource allocation, helping reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Monitoring and analyzing different business processes enables timely issue detection and resolution, lowering operational risks.